Pediatric dentistry
Pediatric Dentistry is a branch of Dentistry that cares for and treats different oral diseases from early childhood to the end of growth. Therefore, the pediatric dentist will be in charge of exploring the child’s oral cavity and detecting possible anomalies in the temporary dentition (baby teeth), as well as applying an individualized procedure and treatment.
The purpose of Pediatric Dentistry is to prevent children from suffering from more serious problems in adulthood. During childhood, parents or guardians, with the help of the dentist, are responsible for transmitting correct hygiene habits to the child to ensure a healthy oral health in the future.

When do the first teeth appear?
The first teeth usually appear at 6 months of age.
- The four front teeth (two above and two below) are the first to appear after 6 months of age.
- By the time he is two and a half years old, all of his baby teeth and molars have erupted.
- There are 20 baby teeth: 10 in the upper jaw and 10 in the lower jaw.
- Remember that the first definitive (permanent) molars come out behind the last milk tooth, around 6 years of age.
Are milk teeth important?
Yes. Baby teeth are very important for the following reasons:
- They allow biting and chewing food.
- They act as a guide for the permanent teeth. Some baby teeth will not fall out until they are 11-12 years old.
- They save space for permanent teeth that will come in later.
- They help pronounce some words.
- They are very important for the child’s self-esteem and for the
smile.
What problems does tooth eruption cause?
In some cases, dental eruption can cause the following problems:
- Red and swollen gums.
- Red cheeks.
- Salivation.
- Disturbed sleep.
Note:
There are teething rings that can be refrigerated and that alleviate the situation. A gentle massage of the gums can also be helpful. Keep in mind that the listed symptoms are not always due to teething. Consult your pediatrician.
Is it true that baby teeth have no root?
No. Like permanent or permanent teeth, milk or temporary teeth also have a root, although this gradually disappears as the moment of tooth loss approaches.
- The tooth is made up of the crown (the part we see) and the root.
- The outermost layer of the tooth is called enamel (1). It is the hardest and most resistant.
- Beneath the enamel is the dentin (2).
- The innermost part is called the pulp (3). In it is the nerve and blood supply to the tooth. The pulp extends from the crown to the tip of the root.
- Surrounding the tooth is the gum (4). The root of the tooth is fixed to the bone (6) through the periodontal ligament (5).
What is the 6 year old molar?
It is the first permanent tooth that normally appears in the mouth around 6 years of age. It is a very important tooth and, unfortunately, many times parents confuse it with a milk tooth.
- The 6-year-old molar comes out behind the two baby molars.
- Its size is much greater than that of milk teeth.
- When it erupts, the two baby molars are still in the mouth.
- It is one of the most important permanent teeth to maintain a correct occlusion.
- It is usually the tooth that is most affected by cavities. The dentist will tell you how to prevent them with fissure sealants.
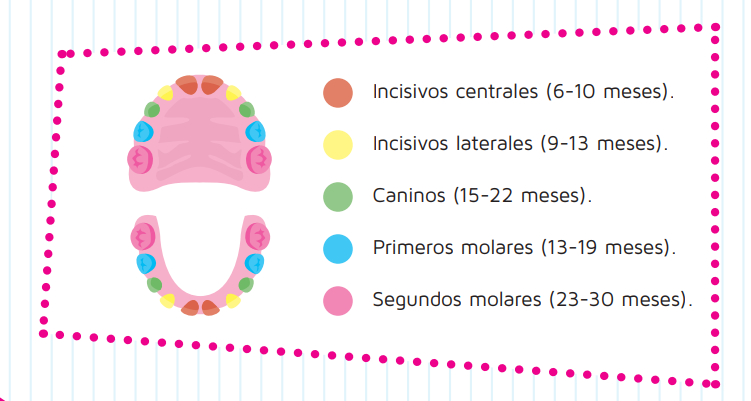
When is it normal for milk teeth to erupt?
The following graph shows the periods considered normal for the eruption of each baby tooth. Keep in mind that there may be some variability from one child to another. Only the dentist will be able to tell you whether or not she is within the normal deadlines.
When can I start cleaning his teeth?
Since your first milk tooth appears, around 6-8 months of age, even earlier, it is highly recommended to start cleaning the gums with a gauze pad and brushing the teeth
- Use a soft pediatric toothbrush and tap water.
- Start using toothpaste early on.
- It is very important to control the amount of paste that is put: only the size of a grain of rice (and spread it over all the bristles).
- Likewise, it is very important to use paste of at least 1,000 ppm from the beginning, as pastes with lower fluoride content have been shown to be ineffective.
- At the age of 3, it is recommended to increase the amount of paste on the brush: now we go to the size of a pea.
- Supervise your children’s tooth brushing and prevent them from swallowing the paste.
- At least two brushings should be done: in the morning and before going to bed.
- The brush should be changed every 3 months or when you notice that the bristles begin to deform.
Is it true that each age corresponds to a type of tooth brushing?
Indeed, depending on the age, a series of concepts must be taken into account:

If my child is not yet 2 years old, how should I clean his teeth?
At these ages, it is the parents who should clean their teeth using a pediatric toothbrush.
smooth and water.
- Consult your dentist: he will explain that you should start with the pediatric brush when the first teeth begin to appear (around 6-8 months).
- Until the eruption of the first teeth (6 months), it is advisable to clean the gums by passing the finger wrapped in a moist gauze.
- From 6-8 months of age, it is already recommended to use toothpaste but the size of a grain of rice. It is important to use a paste of at least 1,000 ppm as it has been shown that lower concentrations of fluoride are not effective in preventing caries.
What should I do if my child is between 2 and 7 years old?
At these ages, parents should supervise tooth brushing. This should be done at least twice a day (in the morning and at night before going to bed). The amount of fluorinated paste depends on age:
- up to 3 years of age, pasta the size of a grain of rice is put on;
- from 3 to 6 years old it increases to the size of a pea
- and from the age of 6, the pasta is increased to the size of a chickpea.
- They should not be rinsed after brushing and make sure they spit out the paste.
- It can be started with the electric brush as it has shown better results in reducing plaque and gingivitis than the manual one.
How often should I replace the toothbrush?
Dentists recommend changing the brush every 3 months because it deteriorates and loses its effectiveness.
- Toothbrushes have a half life and with their use they become deformed, losing their cleaning capacity.
- Sometimes the defoof the bristles is not visible to the naked eye.
- Always remember to rinse the toothbrush very well after each use. It must always be clean.
Is diet important for good oral health in childhood?
Yes. Starting early with healthy dietary habits will help maintain proper oral health, both in the baby teeth and in future permanent teeth.
- Both the amount of sugar in food or drinks and the number of times it is consumed per day are detrimental to dental health.
- Reserve the consumption of sugary products only for meals. Avoid sugary products between meals.
- For snacks between meals use fruits, vegetables, yogurt, cheese or bread.
- Water and milk are the healthiest beverages for teeth. Leave other types of drinks such as bottled juices or soft drinks for exceptional situations and always during meals.
- “Low sugar” or “no added sugar” labels do not mean they are sugar-free.
- The WHO recommends not taking more than 5 teaspoons of sugar per day.
What is a healthy diet for my child?
A diet low in sugar, salt and fat, and high in fruits and vegetables reduces oral diseases and contributes to good general health.
- Remember that eating well is not synonymous with eating a lot. Excess weight and childhood obesity are becoming more frequent in our country.
- Eating well is eating in a balanced way. Do not forget that we are in a country where, traditionally, the Mediterranean diet is used, which is rich in fruits, vegetables and fish.
- Eating well will allow your child to grow healthy. Not only will it help him have a healthy mouth, but it will influence his general health and his growth.
What is caries and how does it develop?
Caries is a destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth (enamel and dentin) due to certain bacteria that transform sugars into acid. If nothing is done, it reaches the pulp (nerve of the tooth), causing pain. An untreated caries can cause infection in other organs of the body (heart, kidney…), in addition to causing tooth loss.
- Caries starts in the enamel, but if nothing is done, it will continue to progress, first into the dentin, until it finally reaches the pulp of the tooth (the nerve).
- At the slightest suspicion of caries, do not delay in taking your child to the dentist.
- Remember that the best prevention of cavities is based on proper dental hygiene, a healthy diet and visits to the dentist.
What is early childhood caries?
Caries in babies and young children is called early childhood caries. It can destroy teeth and occurs mostly in the upper front teeth, although it can affect other teeth. In addition to cavities from the bottle on demand at bedtime, they are also caused by the
frequent contact with sugary drinks, juices, milk (including breast milk on the teeth), due to lack of oral hygiene before bedtime.
- Never dip the pacifier in sugar or honey.
- Do not leave the baby lying down with the bottle, unless it contains water.
- Remember to clean his teeth after every meal and always before going to bed.
Is it true that thumb sucking can cause problems?
Some little ones suck their thumb very hard and this can cause their teeth to shift significantly out of their usual place.
- Most babies like to suck because it gives them pleasure.
- In the long term, this habit can deform the dental arch.
- Educate, little by little, your child to stop the habit.
- From the age of 2, the habit must be suppressed.
- If this is not possible, consult a dentist. He will help you.
Is it true that decay in baby teeth should not be treated because they are going to fall out anyway?
It is totally false. Baby teeth must be treated because they can cause infections, be lost early and create problems later. In addition, the bacteria present in the caries of the baby teeth can also affect the permanent teeth, causing caries in these as well.
- When you notice a cavity in a milk tooth, immediately make an appointment with the dentist.
- The presence of cavities in baby teeth indicates that something is wrong and that action should be taken.
- The dentist, in addition to treating the milk tooth, will give you preventive advice according to your child’s age to avoid new cavities.
- Do not forget that the best guarantee that your child has a healthy permanent dentition is that he also keeps his milk teeth healthy.
When should I take my child to the dentist for the first time?
Ideally, the first visit should take place in the first year of life. also in these.
- This first contact with the dental clinic is fundamental because it will mark future behavior forever. Its objective is to detect and prevent pathologies, early caries or other anomalies. It is very important that we take him as soon as possible so that the child becomes familiar with the dentist and the environment, without waiting to take him when he is ill because the experience will be more negative.